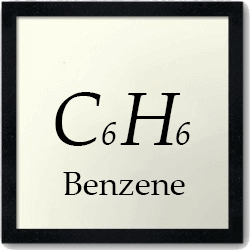
Contaminants
Contaminants
WETS has extensive experience in treating groundwaters and surface waters. The particular characteristics of individual ground and surface water supplies often pose unique contaminant challenges. In our 45 years of experience, working in a range of geographic locations, we have encountered a broad range of primary and secondary water contaminants. We can offer a customized solution to each client’s individual problem. We offer a full spectrum of water treatment needs and our process solutions are backed by the demonstrated success of hundreds of installations throughout Texas and neighboring states. WETS can offer a pilot study program to optimize an existing plant or to assist in the design of a new plant.

Our Applications
Since well water is typically not exposed to air, dissolved iron and manganese compounds, on exposure to air, readily oxidize to form insoluble reddish-brown particles. These particles discolor the water and cause problems with laundry and plumbing fixtures. WETS has extensive experience in water treatment for iron removal; we have provided treatment equipment, or entire treatment systems, for dozens of projects through our years of operation.
Solutions to Your Water Treatment Needs
Whether you want a new water treatment system installed, need your current one inspected and repaired, or just want a free quote, contact the WETS LLC. With years of experience in the industry, our skilled team members are trained and knowledgeable with a variety of leading water equipment and products. Our certified water purification experts are here to help.